Learn about data recovery
File Storage: Sectors and Clusters
When you purchase a new hard drive and before it has any data on it, it is has usually already undergone a 'low level format'. The purpose of a low level format is to divide all the magnetic space on the hard drive into small storage areas. These storage areas are known as 'sectors', however for efficiency purposes the Operating System (e.g. Windows XP) groups sectors together into 'clusters'.
A cluster is the smallest unit of storage space with which the Operating System (e.g. Windows XP) will deal. If you save a very small file to your computer it will all fit within 1 storage cluster on the hard drive. If you save a very large file it may fill up many clusters, that is, as many clusters as it takes to hold all the content of the file.
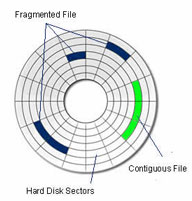
Things get a bit more complicated by the fact that a single file does not have to reside within contiguous clusters. It may be that the Operating System stores a single file in clusters on different parts of the hard disk. This is called a 'fragmented' file. The problem with a fragmented files is that it can slow your computer down as it needs to spend time and resources sending the actuator arm to different parts of the hard disk to read the complete file. This is why many people regularly use a defragmentation program. The amount of fragmentation in a file can also reduce your ability to recover deleted files as we will explain later in this article.
So we can now think of our hard drive as being broken down into many clusters which hold the contents of our files. A cluster that is being used to store a file is called an 'allocated cluster', and if it is not being used to store a file an 'unallocated cluster'.
The next question is, 'how does the computer know where to look when it wants to find a specific file?'. Well, if you wanted to find a specific chapter in a book the best thing to do would be to go and look up the Table of Contents. A computer does much the same thing.
Next article: NTFS and FAT data recovery
Previous article: Hardware recovery

Recover My Files download instructions
- Click the download button to begin the download.
- If possible, save then install the Recover My Files installation program on a drive other than the one on which your files were lost.
- Run Recover My Files, search your drive and preview the files found in the results screen.
- NOTE: Software will only run on Windows PC's
» Previous Versions